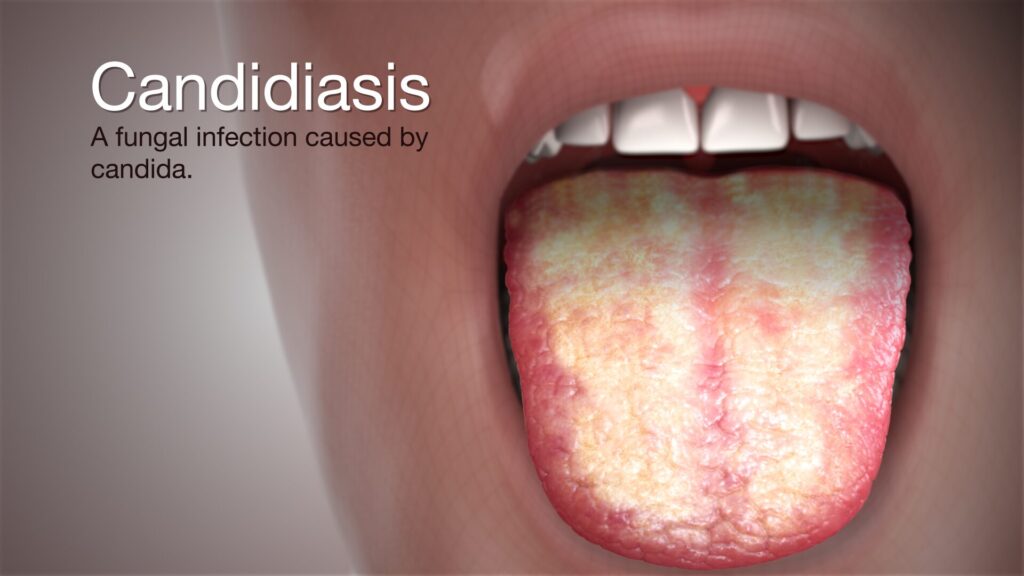
Candida infections are one of the most common health challenges that women face, yet they are often misunderstood or overlooked in broader discussions about women’s health 念珠菌. Candida is a type of yeast that naturally exists in the human body, usually in the mouth, gut, and vaginal area. In normal circumstances, it remains balanced by the body’s natural flora and immune system. However, when the balance is disturbed, Candida can multiply and cause an infection known as candidiasis. Addressing this issue is a vital aspect of women healthcare, as it impacts physical comfort, reproductive health, and overall well-being.
Understanding Candida in Women
Candida infections, particularly vaginal yeast infections, are prevalent among women. Nearly every woman will experience some form of yeast infection during her lifetime. While Candida albicans is the most common strain responsible for these infections, other strains may also cause discomfort and complications. Recognizing the symptoms, understanding the causes, and adopting effective preventive measures are all essential steps in promoting better women healthcare outcomes.
The most common symptoms of Candida overgrowth in women include itching, burning, abnormal discharge, swelling, and discomfort during urination or intercourse. These symptoms, while not usually life-threatening, can significantly affect quality of life if not treated properly.
Causes of Candida Overgrowth
Several factors can disrupt the balance of yeast and bacteria in the body, leading to Candida infections. Antibiotic use, for example, is a major contributor since antibiotics often eliminate the healthy bacteria that keep yeast growth in check. Hormonal changes, such as those occurring during pregnancy, menstruation, or menopause, can also increase vulnerability. Additionally, high levels of stress, poor diet, weakened immunity, or uncontrolled diabetes may trigger Candida overgrowth.
Lifestyle choices, including wearing tight, non-breathable clothing or using scented feminine hygiene products, can further exacerbate the problem. This highlights how closely Candida management is tied to women healthcare practices that prioritize preventive care and awareness.
The Role of Candida in Women Healthcare
Women healthcare is not only about addressing visible conditions but also about understanding the hidden or recurring health issues that affect daily life. Candida infections are a prime example of a recurring problem that can lead to frustration if not properly managed. By incorporating Candida education into women healthcare initiatives, women can feel more empowered to recognize early signs and take action.
Healthcare providers often emphasize the importance of maintaining vaginal health, and Candida management plays a significant role in this context. Regular checkups, discussions about sexual health, and guidance on maintaining a healthy lifestyle all contribute to reducing the occurrence of infections.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Candida
Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment. Many women may assume they have a yeast infection based on symptoms alone, but other conditions, such as bacterial vaginosis or sexually transmitted infections, can present with similar signs. A proper medical evaluation ensures correct treatment and prevents mismanagement.
Once diagnosed, treatment options include antifungal medications, which may be prescribed as oral tablets, topical creams, or suppositories. In cases of recurrent Candida infections, doctors may recommend a longer treatment course or lifestyle adjustments to address underlying causes.
Natural remedies are also becoming popular among women seeking alternative healthcare solutions. Probiotics, for instance, help restore the natural balance of bacteria and yeast in the body. Dietary changes, such as reducing sugar intake, can also play a role in preventing Candida overgrowth, since yeast thrives on sugar.
Candida and Lifestyle Management
Effective Candida management requires more than just medication. Lifestyle adjustments form a cornerstone of preventive women healthcare. Wearing breathable cotton underwear, avoiding prolonged damp clothing, and practicing good hygiene without overuse of chemical-based products can significantly reduce risks.
Diet also plays an essential role. A nutrient-rich diet that includes vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and probiotics supports immune health and discourages Candida growth. At the same time, reducing processed foods, refined sugar, and alcohol helps maintain balance in the body.
Stress management is equally important. High stress levels weaken the immune system, making women more vulnerable to infections. Incorporating practices such as yoga, meditation, or simply ensuring adequate rest can support overall women healthcare while lowering the risk of Candida overgrowth.
Emotional and Social Impact of Candida
Candida infections do not only cause physical discomfort but also have emotional and social impacts. Persistent itching, burning, or discomfort during intimacy can affect relationships and self-confidence. Women may feel embarrassed or hesitant to seek medical help, which can prolong the condition and worsen symptoms.
By promoting open discussions around Candida in women healthcare, healthcare providers can help remove stigma and encourage women to seek timely care. Education campaigns, support groups, and accessible resources play a vital role in normalizing conversations about vaginal health and encouraging preventive measures.
Candida in Special Health conditions
Women with chronic illnesses such as diabetes are more prone to Candida infections due to elevated blood sugar levels, which provide an ideal environment for yeast growth. Similarly, women undergoing cancer treatments or those with weakened immune systems are at higher risk. For these women, Candida management is an integral part of comprehensive healthcare.
Pregnant women may also experience a higher likelihood of yeast infections due to hormonal changes. While usually harmless to the baby, untreated infections can cause significant discomfort to the mother. Hence, prenatal care that includes monitoring and managing Candida is an important aspect of women healthcare.
The future of Candida Management in Women Healthcare
With advances in medical research, there is a growing focus on developing better diagnostic tools and more effective treatments for Candida infections. Personalized healthcare approaches are being explored, recognizing that each woman’s body responds differently to treatment. Innovations in probiotics, natural therapies, and lifestyle-based healthcare models are expected to play an increasingly important role in women healthcare.
Furthermore, digital healthcare platforms are making it easier for women to access information, consult doctors, and manage their health proactively. Telehealth services, educational resources, and wellness apps are transforming how Candida and other women’s health issues are addressed.
Conclusion
Candida is a common yet often underestimated condition that deeply influences women healthcare. While it may appear as a simple yeast infection, its impact on physical, emotional, and social well-being is significant. Addressing Candida requires a holistic approach that combines medical treatment, lifestyle adjustments, and greater awareness.
By incorporating Candida management into broader women healthcare strategies, women can achieve better health outcomes, greater comfort, and improved quality of life. Breaking the stigma, promoting education, and empowering women to take charge of their health are essential steps toward ensuring that Candida no longer remains a silent disruptor of women’s well-being.